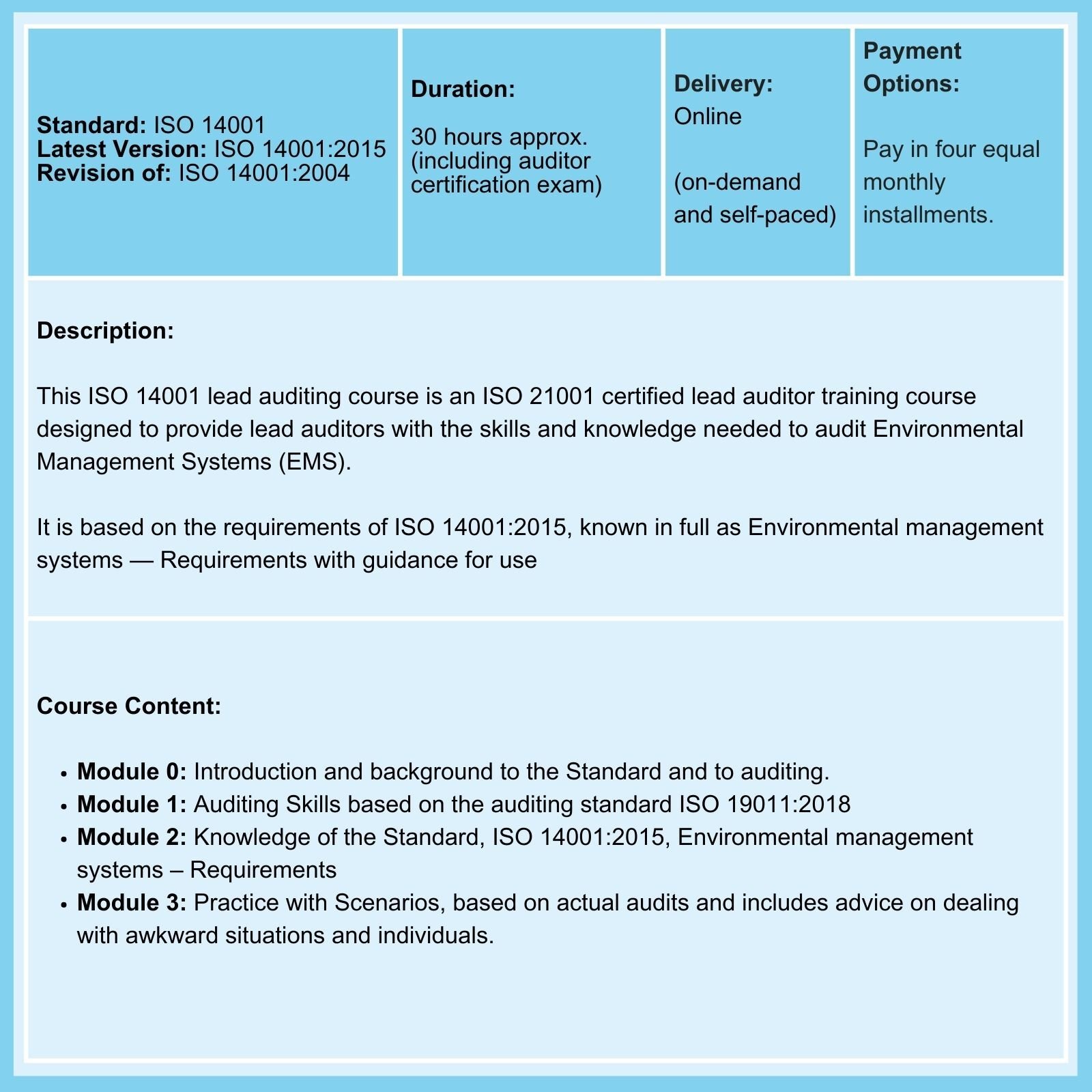
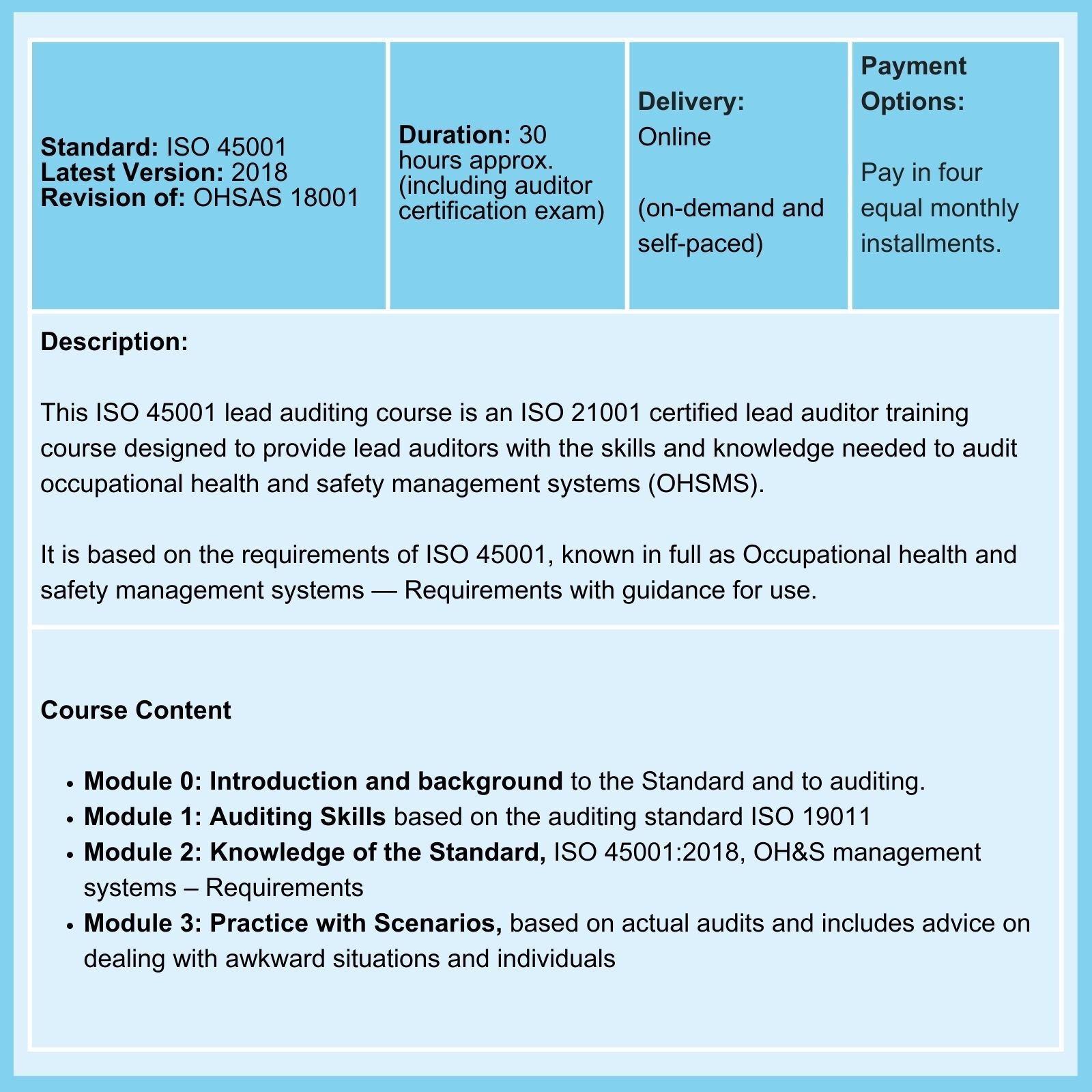
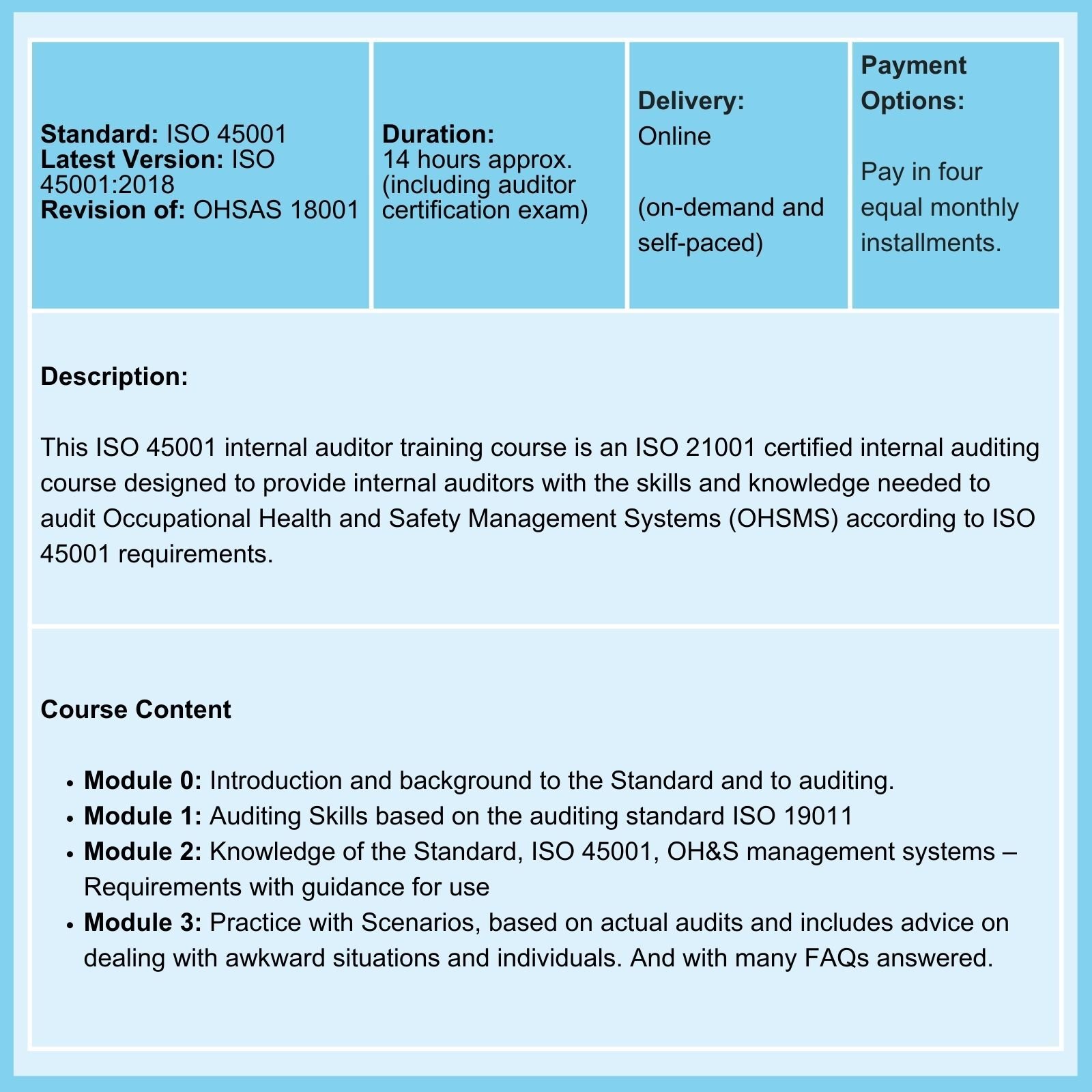
Being in a professional ISO auditor register isn't enough
Competence is defined as the ‘ability to apply knowledge and skills to achieve intended results.’ And so it is with ISO Auditor Competence. Your Lead Auditor Certificate alone does not ensure competence. Nor, when competent, do you suddenly become incompetent three years after receiving your certificate.
Confused? Don't be. For Lead Auditors and their Audit Team Members, the requirements for competency have been defined in ISO standards.
Who sets the criteria and evaluates and decides on ISO Auditor competence?
In clause 4.3.3 of ISO 17021-1, the ISO Standard for Certification Bodies, competency is a crucial requirement for the certification body to have an implemented process for establishing competence criteria. These criteria will be used for the personnel involved in the audit and other certification activities and to perform evaluations against them.
Also, 'the certification body shall have processes for selecting, training, formally authorizing auditors and for selecting and familiarizing technical experts used in the certification activity.'
The initial competence evaluation of an auditor, by the Certification Body, ‘shall include the ability to apply required knowledge and skills during audits, as determined by a competent evaluator observing the auditor conducting an audit.’ Clearly, ISO training alone is not enough.
Do you have what it takes to be a Lead Auditor?
Auditors are required to demonstrate specific knowledge and skills, including the following:
For Audit Team Members
- Knowledge of specific management system standards/normative documents
- Knowledge of the certification body’s processes
- Knowledge of the client’s business sector
For Lead Auditors, in addition to the four Knowledge and Skillsets, the following are also required:
- Knowledge of business management practices
- Knowledge of audit principles, practices, and techniques
- Knowledge of client products, processes, and organization
- Language skills appropriate to all levels within the client organization
- Note-taking and report-writing skills
- Presentation skills
- Interviewing skills
- Audit-management skills
Auditor competence, therefore, goes beyond a knowledge of the standard or the completion of a Certified Auditor Course.
So, what knowledge and skills must a Lead Auditor demonstrate?
Can a Training Organization or a professional body determine an ISO Auditor's competence?
No! The two things to note are...
- in determining competence, the auditor must be observed conducting an audit and
- the Certification Body must provide the observer.
So, as required by ISO 17021-1, this is the responsibility of the Certification Body, which decides on an auditor's competence and maintains evidence of such competency.
Must an ISO Auditor maintain an Auditor's Log and be re-trained or re-certified every three years?
Again, no! There are no such requirements in ISO 17021-1. The certification body must, of course, ensure the auditor's ongoing competence. Re-training, conversion training, and the extension of scope (add other ISO standards) may be part of maintaining competence. Experience over 25+ years tells us that practical and frequent experience in carrying out audits is a more significant component in maintaining competency than training.
Certified Auditor Training is essential, but it is only one step toward becoming a competent ISO Auditor.
For a bit of fun, assess your Auditing Skills.
Are you curious how your auditing skills are measured against ISO standards? Try our internal auditor skills checker for free by clicking the button below.
For further information
If you'd like more information, you can just try these links.
- ISO 19011: 2011 - Guidelines for auditing management systems
- ISO 17021-1: 2015 - Conformity assessment -- Requirements for bodies providing audit and certification of management systems -- Part 1: Requirements
- ISO/IEC TS 17021-2:2012 - Part 2: Competence requirements for auditing and certification of environmental management systems
- ISO/IEC TS 17021-3:2013 - Part 3: Competence requirements for auditing and certification of quality management systems
Related Courses
Related Articles
- 5 Reasons Why Assessing the Competence of Auditors is a Must
- Why training your ISO Internal Auditors is a ‘Must’
- ISO 9001 Competence, Awareness, and Communication
- How to become an ISO Lead Auditor
deGRANDSON Global is an ISO Certified Educational Organization
In October 2021, we secured certification to three education-related ISO Standards. We now have a university-grade management system in place conforming to the requirements of …
We have chosen ISO 21001 certification because, unlike IRCA and Exemplar badges (which, in our opinion, are commercially compromised), it is based on independent third-party assessment. It is a ‘university grade’ standard used globally by schools, colleges, and universities to demonstrate their competence.
We offer Courses for ISO 9001, ISO 13485, ISO 14001, ISO 17025, ISO 27001, ISO 45001, Data Protection, Risk Management, and more.