There are many popular data security standards other than ISO 27001
Frequently, cybersecurity standards other than ISO 27001 and the 47+ subsidiary standards of the ISO 27000 series are incorporated into Information Security Management Systems (ISMSs). Auditors of ISMS and those negotiating with customers on information security issues need knowledge of and the use/application of these standards.
While our ISO 27001 training courses don't cover these standards, we will discuss here some of the most common standards that you will encounter. We will consider each of the Standards and Guidelines in alphabetical order.
Table of Contents
Click to expand
- CIS Controls
- COBIT
- COSO - The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission
- DORA
- EU GDPR - General Data Protection Regulation - EU
- FIPS – Federal Information Processing Standards
- FISMA – The Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002
- HIPAA - The US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
- ISO 27701
- NHS-DSPT - UK
- NIST CSF - NIST Cybersecurity Framework
- PCI-DSS - the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard
- SOC - System and Organization Controls
- SOX – The Sarbanes–Oxley Act of 2002
- UK GDPR - General Data Protection Regulation - UK
Note: Click on the titles above to be taken to the relevant section of this post.
Familiarizing Yourself with Other Information Security Standards
Before considering each standard and guideline, let's examine their relationship with ISO 27001. Whether you are part of a Certification Body Audit Team or a member of an internal Audit Team, you will need, as part of the document review in preparation for the audit, to familiarize yourself with the other security data standards to which the organization subscribes.
Such standards, where they apply (by choice or by contractual obligation), must be incorporated into the ISMS and included in the Audit Scope. And this, in addition to any applicable ISO standards from the ISO 27000 series other than ISO 27001 and ISO 27002, which automatically apply.
Yes, you can expect to spend considerable time reading yourself into an ISO 27001 audit. Or prepare yourself for negotiations with a security-conscious customer or prospect (or you might choose to use the services of an expert).
And, of course, all of this also applies if you are involved in implementing and maintaining an Information Security Management System in compliance with ISO 27001.
CIS Controls
CIS Controls are a set of best practices developed by the Center for Internet Security to help organizations improve their cybersecurity. They consist of 18 prioritized actions that guide organizations in protecting systems and data from known cyber threats. These controls include inventorying assets, securing configurations, managing access, monitoring activity, and responding to incidents. Designed to be practical and effective, the CIS Controls are updated regularly based on real-world threat data and input from cybersecurity experts.
COBIT - Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology
COBIT is not a standard as such, but is a framework that links IT initiatives to business requirements, organizes all IT activities into an accepted business practice model, identifies information resources to be utilized and leveraged, and defines the management control objectives.
While COBIT may contain ISO and PCI-DSS standards, it is more concerned with compliance to ensure that all activities, acquisitions, and management activities fall within the accepted norms of doing things.
It is accepted globally as a guidance tool for the good governance of the business for IT and related technologies.
COSO - The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission
COSO is a joint initiative of five private sector organizations and is dedicated to providing thought leadership through the development of frameworks and guidance on enterprise risk management, internal control, and fraud deterrence.
In 2013, COSO updated the document ‘Internal Control-Integrated Framework’. COSO’s goal in updating the framework was to increase its relevance in the increasingly complex and global business environment so that organizations worldwide can better design, implement, and assess internal control.
DORA - Digital Operational Resilience Act - EU
DORA is an EU regulation aimed at strengthening the IT security and resilience of financial entities. It ensures that firms can withstand, respond to, and recover from all types of ICT-related disruptions and threats. DORA standardizes requirements for risk management, incident reporting, digital operational resilience testing, third-party risk, and information sharing across the EU’s financial sector. Effective from January 2025, it applies to banks, insurers, investment firms, and ICT service providers. DORA enhances financial stability by enforcing consistent rules for managing digital risks in an increasingly interconnected and technology-driven environment.
EU GDPR - General Data Protection Regulation - EU
The EU GDPR is a comprehensive data privacy law that governs how organizations collect, use, and protect the personal data of individuals in the European Union. Enforced since May 2018, it gives individuals greater control over their data, including rights to access, correct, delete, and restrict processing. GDPR applies to any organization processing EU residents’ data, regardless of location. It mandates clear consent, data protection by design, breach notifications, and accountability. Non-compliance can result in heavy fines. GDPR aims to harmonize data privacy laws across the EU and enhance individual privacy rights in the digital age.
FIPS – Federal Information Processing Standards
FIPS are publicly announced standards developed by the United States federal government for use in computer systems by non-military government agencies and government contractors.
They establish requirements for various purposes, such as ensuring computer security and interoperability, and are intended for cases in which suitable industry standards do not already exist.
Many FIPS specifications are modified versions of standards used in the technical communities, such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
FISMA – The Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002
FISMA is a US federal law that recognises the importance of information security to the economic and national security interests of the United States.
FISMA has brought attention to cybersecurity within the federal government and explicitly emphasized a "risk-based policy for cost-effective security." It requires agency program officials, chief information officers, and inspectors general (IGs) to conduct annual reviews of the agency’s information security program and report the results to the Office of Management and Budget (OMB).
HIPAA - The US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, 1996
HIPAA is a U.S. law enacted to protect sensitive patient health information. It sets national standards for the privacy, security, and confidentiality of medical records and personal health data. HIPAA applies to healthcare providers, insurers, and business associates that handle protected health information (PHI). Key rules include the Privacy Rule, Security Rule, and Breach Notification Rule, which govern data use, safeguarding measures, and mandatory reporting of data breaches. HIPAA ensures patients’ rights over their health information while enabling the secure flow of data needed for high-quality healthcare and system efficiency.
ISO/IEC 27701
ISO/IEC 27701 is an extension to the ISO/IEC 27001 and 27002 standards, focusing on managing personally identifiable information (PII). It provides guidelines for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving a Privacy Information Management System (PIMS). Designed for data controllers and processors, it helps organizations comply with privacy regulations like GDPR by integrating privacy into their existing information security framework. ISO 27701 outlines roles, responsibilities, and controls for protecting PII, promoting transparency and trust. It supports risk-based privacy management and helps demonstrate accountability in handling personal data across various jurisdictions and business contexts.
NHS DSPT - The NHS Data Security and Protection Toolkit - UK
NHS DSPT is an online self-assessment tool for UK health and care organizations to measure their data security and compliance with the National Data Guardian’s standards. It ensures that organizations handle personal data safely and meet legal and regulatory requirements, including the Data Protection Act and GDPR. The DSPT covers areas such as data protection, IT security, staff training, and incident management. Completion is mandatory for NHS partners and suppliers accessing NHS data or systems, helping to maintain trust, transparency, and high standards of information governance across the healthcare sector.
NIST CSF - NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The NIST CSF is a voluntary set of guidelines developed by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology to help organizations manage and reduce cybersecurity risk. It consists of five core functions—Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover—providing a structured approach to improving cyber resilience. The framework is flexible, adaptable, and widely used across industries and sectors, regardless of size or maturity. It promotes risk-based decision-making, supports regulatory compliance, and facilitates communication between technical and non-technical stakeholders. NIST CSF is a global benchmark for building strong, proactive cybersecurity programs tailored to an organization’s specific needs and risks.
PCI-DSS - The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard
PCI DSS is a global security standard designed to protect cardholder data and reduce credit card fraud. Developed by the PCI Security Standards Council, it applies to all organizations that store, process, or transmit payment card information. PCI DSS includes requirements for secure network architecture, access controls, encryption, monitoring, and vulnerability management. Compliance is mandatory for businesses handling card payments and is enforced by major credit card brands. By following PCI DSS, organizations strengthen their data security posture, build customer trust, and reduce the risk of data breaches and financial penalties.
SOC - System and Organization Controls
SOC, defined by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), is the name of a suite of reports produced during an audit. It is intended for use by service organizations to issue validated reports of internal controls over those information systems to the users of those services.
The reports focus on controls grouped into five categories called Trust Service Principles. Additional AICPA guidance materials specify three types of reporting. The 5 Trust Service Principles are ...
- Privacy,
- Security,
- Availability,
- Processing Integrity and
- Confidentiality.
And the three types of SOC reports are:
- SOC 1 (Internal Control over Financial Reporting - ICFR),
- SOC 2 (Trust Services Criteria) and
- SOC 3 (Trust Services Criteria for General Use Report).
These Reports continue to be very popular and are frequently asked for by prospective customers.
SOX – The Sarbanes–Oxley Act of 2002
SOX, commonly called Sarbanes–Oxley, Sarbox or SOX, is a United States federal law that sets new or expanded requirements for all U.S. public company boards, management, and public accounting firms.
There are also a number of provisions of the Act that also apply to privately held companies, for example, the willful destruction of evidence to impede a Federal investigation.
The Act, which contains eleven sections, was enacted as a reaction to a number of major corporate and accounting scandals, including Enron and WorldCom.
It sets out the responsibilities of a public corporation’s board of directors, adds criminal penalties for certain misconduct, and requires the Securities and Exchange Commission to create regulations to define how public corporations are to comply with the law.
UK GDPR - General Data Protection Regulation - UK
UK GDPR is the United Kingdom’s data protection law that governs how personal data is collected, used, and stored. It mirrors the EU GDPR, which it replaced post-Brexit, and works alongside the UK Data Protection Act 2018. UK GDPR gives individuals rights over their data, including access, correction, deletion, and objection to processing. It applies to any organization processing personal data of UK residents, regardless of location. The law requires transparency, accountability, lawful processing, and strong data security measures. Non-compliance can result in significant fines. UK GDPR aims to protect privacy while enabling responsible data use in the digital economy.
A Point to Note:
ISO 27001 has the capacity to incorporate one or more of the standards and guidelines we have considered here, that is, the ISMS as an integrated management system. It is not unusual, however, for the applicable IS standards and guidelines to be documented and implemented separately. The choice is yours.
Related Courses
Related Courses
Related Articles
- How does ISO 27001:2022 compare with ISO 27001:2013?
- Free ISO 27001 Implementation Handbook (100+ pages)
deGRANDSON Global is an ISO-certified Educational Organization
We have chosen ISO 21001 certification because, unlike IRCA and Exemplar badges (which, in our opinion, are commercially compromised), it is based on an independent third-party assessment. It is a ‘university grade’ standard in use globally by schools, colleges, and universities to demonstrate their competence.
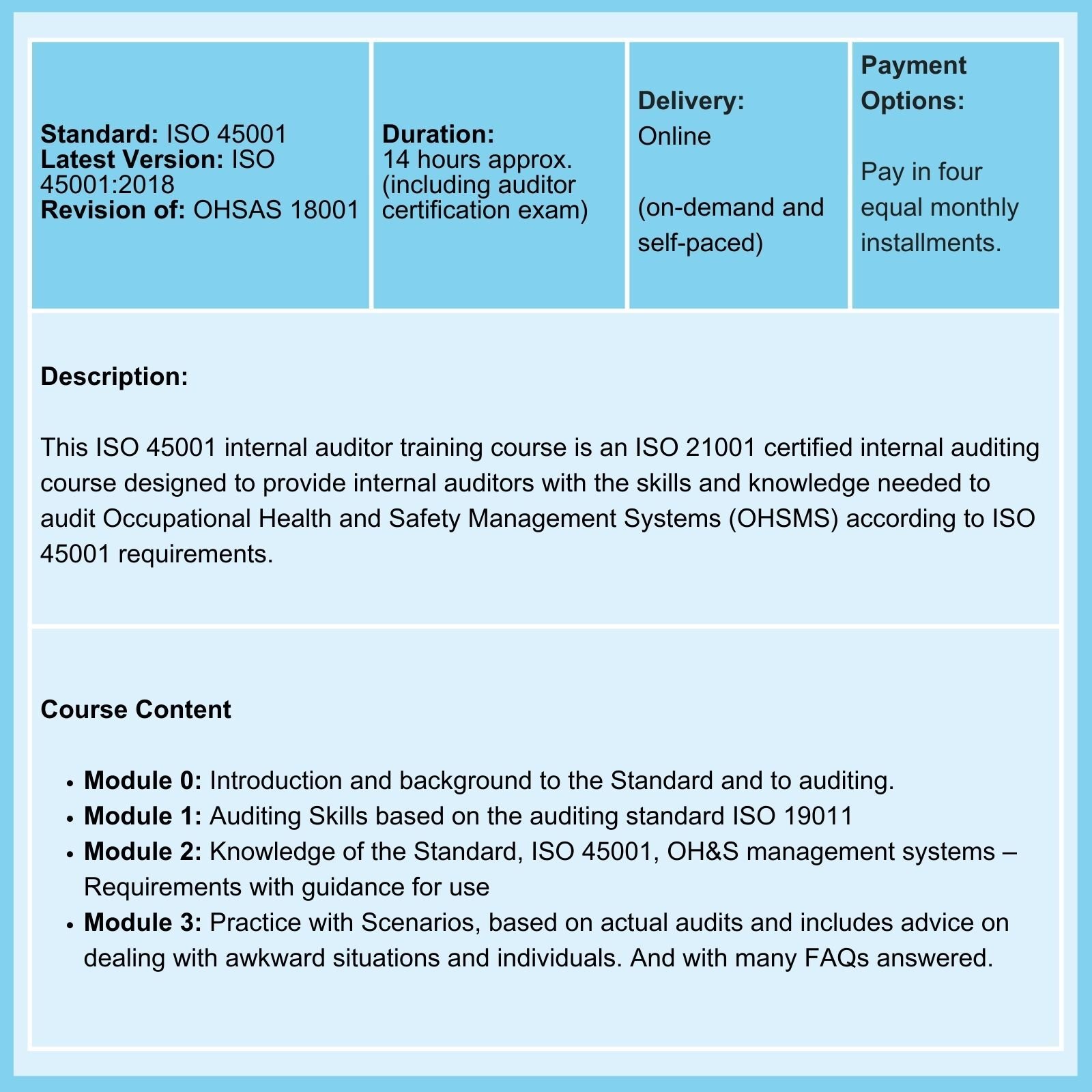
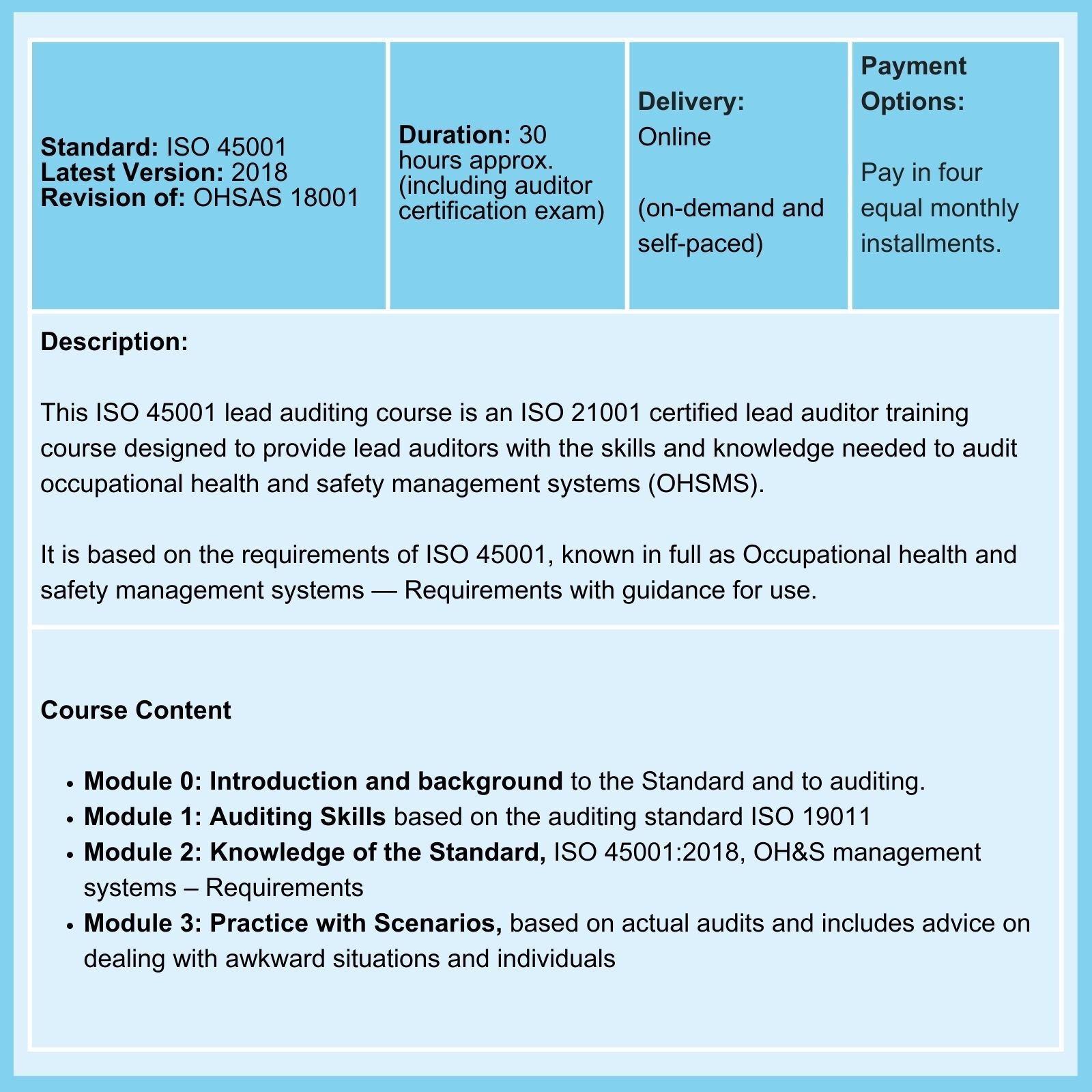
We offer Certified Courses for ISO 9001, ISO 13485, ISO 14001, ISO 17025, ISO 27001, ISO 45001, Data Protection, and Risk Management.