Systematically identifying relevant ISO 14001 environmental aspects in implementing an EMS.
This is fundamental to the effectiveness of an Environmental Management System (EMS) and to ensuring that your organization meets ISO 14001 certification requirements.
Definition of Environmental Aspects
Environmental Aspects refer to the elements of an organization's activities, products, or services that interact with the environment.
Identifying and understanding Environmental Aspects is a vital step in developing and implementing an Environmental Management System (EMS) that complies with the requirements of ISO 14001.
ISO 14001 and Environmental Aspects
ISO 14001 provides a structured framework for identifying, assessing, and managing environmental aspects. It ensures that organizations minimize their environmental footprint and adhere to sustainable practices.
Below are some critical points in ISO 14001 that relate to Environmental Aspects.
- Identification: Identify all aspects of your activities, products, and services that may interact with the environment. This includes both direct and indirect aspects.
- Assessment: Each identified environmental aspect should be evaluated to determine its significance. Significance is typically determined by considering the potential environmental impacts of the aspects, their frequency of occurrence, and the legal and regulatory requirements associated with them.d
- Impact Evaluation: Environmental aspects can have both positive and negative impacts on the environment. Accordingly, you should assess and prioritize these aspects based on their potential to harm or benefit the environment.
- Documentation: ISO 14001 requires organizations to document their process for identifying and assessing environmental aspects. This documentation is typically part of the EMS and includes the criteria for evaluating significance.
- Monitoring and Control: You must establish controls and procedures to manage and mitigate significant environmental impacts. This may involve setting objectives and targets for improvement, implementing operational controls, and monitoring progress.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with applicable environmental laws and regulations is essential to managing environmental aspects. You must ensure that your organization complies with all applicable legal requirements across its key areas.
- Continuous Improvement: ISO 14001 promotes a commitment to continual improvement. Therefore, it is important to regularly review and reassess your company's environmental aspects and their significance to adapt to changing circumstances and improve your environmental performance.
Why are Environmental Aspects Important to ISO 14001 Implementation?
Environmental Aspects, as outlined in Clause 6.1.2, are essential to implementing ISO 14001. This is because failing to include them will:
- They undermine EMS's credibility with stakeholders (if a customer spots a significant omission, what will that say to them about your organization?); represent a loss to your business (perhaps a considerable cost-saving opportunity missed); and cause unnecessary environmental damage.
- Also, as an ISO 14001 Lead Implementer or EMS Consultant, you will not want to leave significant omissions for an External Auditor to find. You will want an environmental aspects and impacts register that is ISO 14001 compliant.
Examples of Environmental Aspects
Environmental aspects cover various elements of an organization's activities, products, or services that interact with the environment. By identifying and understanding these aspects, you can effectively integrate environmental considerations into your operations in accordance with ISO 14001 standards.
Here are some examples of environmental aspects you need to know...
- Energy Usage encompasses energy consumption, such as electricity and fuel, within an organization's operations. Energy use can have a significant environmental impact, particularly if it relies on non-renewable energy sources.
- Water Quality Management: Organizations that discharge wastewater into water bodies must consider the impact on water quality and ecosystems.
- Emissions: Emissions of greenhouse gases (e.g., carbon dioxide), air pollutants (e.g., sulfur dioxide), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are critical, particularly for industries with combustion processes or chemical operations.
- Waste Management: The generation of solid, hazardous, or wastewater is a common environmental concern. Proper waste management and recycling efforts can help mitigate the environmental impact.
- Chemical Usage: Chemical use and handling in manufacturing, cleaning, or other processes can impact the environment. Managing chemical use and minimizing spills or releases are critical.
- Biodiversity Impact: Activities that encroach on natural habitats, deforestation, or pollution that affect local ecosystems and wildlife are also environmental aspects.
- Noise Pollution—Noise and vibrations from industrial processes or construction activities are environmental impacts. Noise pollution prevention, therefore, must be carefully planned if your organization operates in areas with sensitive ecosystems or residential neighborhoods.
- Resource Depletion: Aspects related to the depletion of natural resources, such as minerals, timber, or fossil fuels, are important to consider in the context of sustainability and environmental impact.
- Land Use and Land Contamination: The use of land for industrial or agricultural purposes and potential land contamination from chemicals or pollutants are significant aspects.
- Packaging and Product Design: Material selection and product and packaging design can influence environmental impact, including resource use, emissions, and waste generation.
- Transportation: For organizations involved in transportation, vehicle type, fuel efficiency, and maintenance practices are environmental considerations.
- Sustainable Procurement: The selection of suppliers, materials, and products can affect environmental impact. Ensuring sustainable, eco-friendly procurement practices is important.
How to Identify the Environmental Aspects of Your Organisation
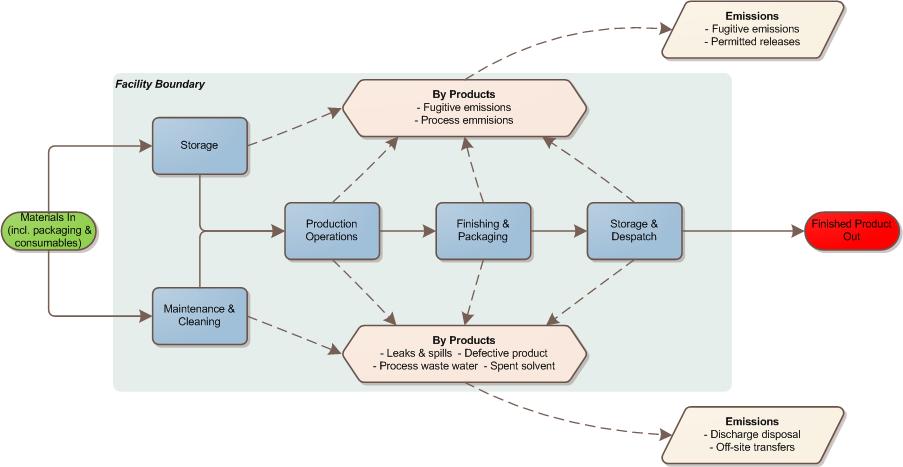
Look at the Process from a Life Cycle Perspective
When implementing ISO 14001:2015, identifying all applicable environmental aspects is fundamental. When determining those environmental aspects, you must consider a life-cycle perspective. The applicable life-cycle stages vary by activity, product, or service.
You need to determine or re-determine the environmental aspects within the scope of the environmental management system. Consider the inputs and outputs (both intended and unintended) associated with current and relevant past activities, products, and services; planned or new developments; and new or modified activities, products, and services.
In the future, this will require new or revised systems of work. How, for example, will your EMS address remote work, which falls within its scope?
Know What to Include in Your Organization's Environmental Aspects
The method should consider normal and abnormal operating conditions, shutdown and start-up conditions, and reasonably foreseeable emergencies. Attention should be paid to prior emergency incidents.
You do not have to consider each product, component, or raw material individually to determine and evaluate its environmental aspects. When they have common characteristics, you may group or categorize activities, products, and services.
Look Into the Environmental Aspects that Your Organization Can Influence
An organization determines whether there are environmental aspects it can influence, in addition to those it can control directly.
These can relate to products and services used by the organization, provided by others, or offered to others, including those associated with outsourced processes.
It can have a limited influence on the use and end-of-life treatment of products and services provided to others.
Ultimately, the organization determines the extent of control it can exercise, the environmental aspects it can influence, and how much influence it chooses to exercise.
Seek Help with Identifying Other Environmental Aspects
It is unlikely that one person can satisfactorily complete this exercise alone. A team of people with relevant experience and expertise is needed. The Team you need will primarily work for your organization, but external experts may also be required.
If you need further clarification, talk to a reputable expert or consultant and to their clients before engaging their services. Begin by identifying Environmental Aspects by brainstorming with your Team.
And deGRANDSON Training will always help...
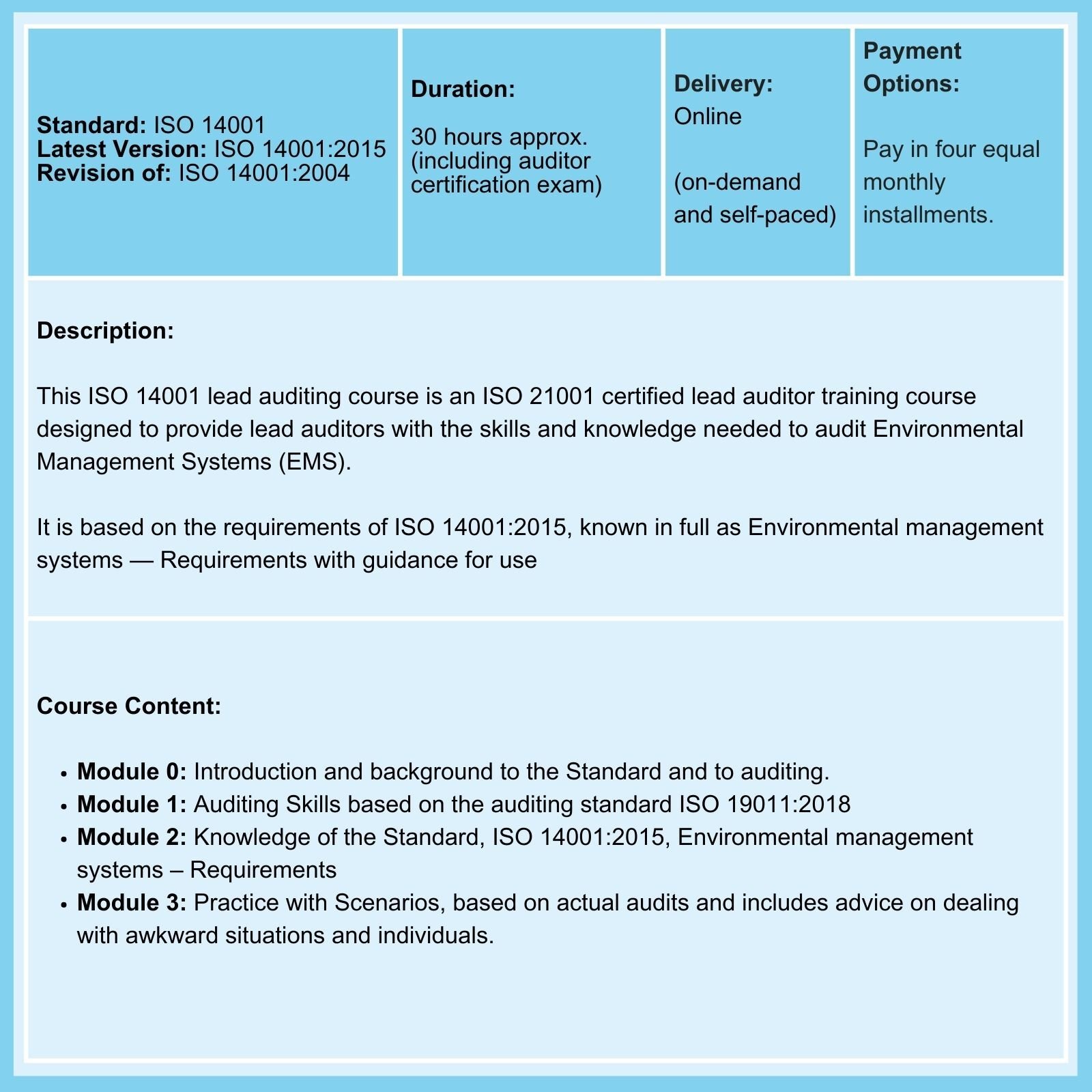
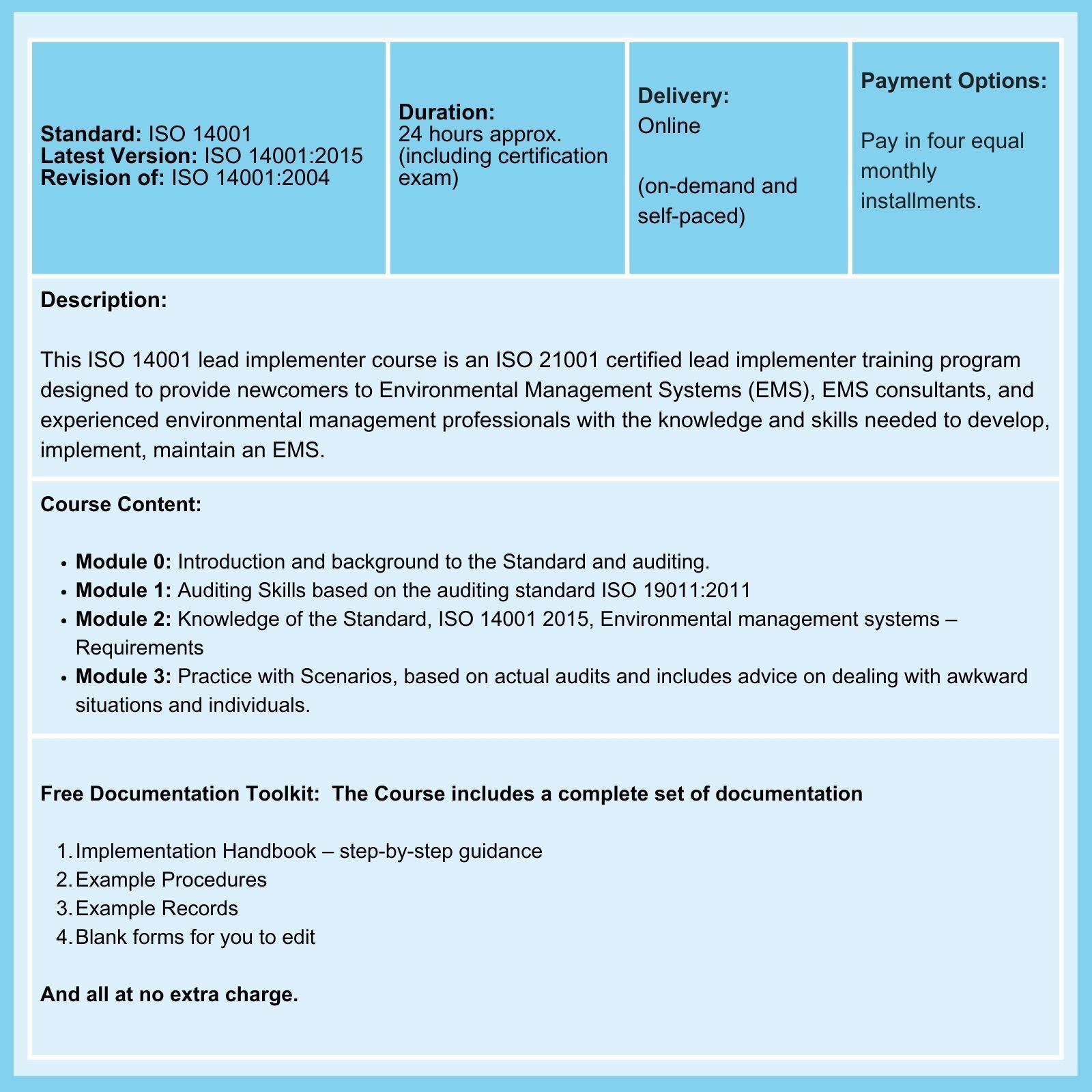
One of our ISO 14001 Series of Courses, ISO 14001 Lead Implementer, includes detailed identification, risk analysis, and risk treatment of Environmental Aspects.
Alternatively, suppose you want a quick refresher on ISO 14001. In that case, you can also find answers to frequently asked questions about the standard, the training, and the certification process on our ISO 14001 course overview page.
Related Courses
Related Articles
- The ISO 14000 Family of Environmental Standards
- ISO 14001 Consultancy: How to be an EMS Consultant?
- How to do an ISO 14001 Gap Analysis
- Preparing for an ISO 14001 Certification Audit
- ISO 14001 Free Implementation Handbook (100+ pages)
deGRANDSON Global is an ISO Certified Educational Organization
In October 2021, we secured certification to three education-related ISO Standards. We now have a university-grade management system in place that conforms to the requirements of …
We have chosen ISO 21001 certification because, unlike IRCA and Exemplar badges (which, in our opinion, are commercially compromised), it is based on independent third-party assessment. It is a 'university grade' standard globally by schools, colleges, and universities to demonstrate their competence.
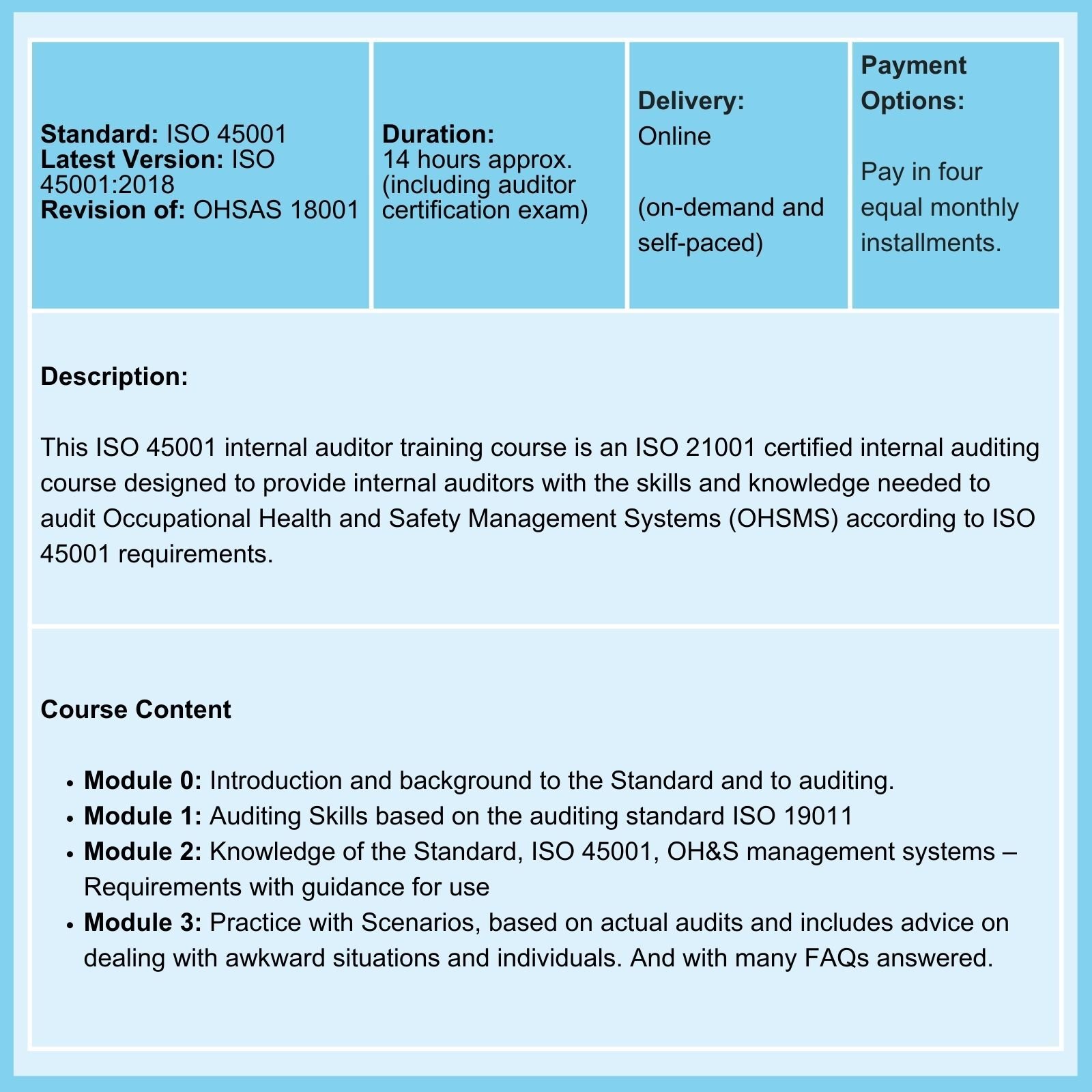
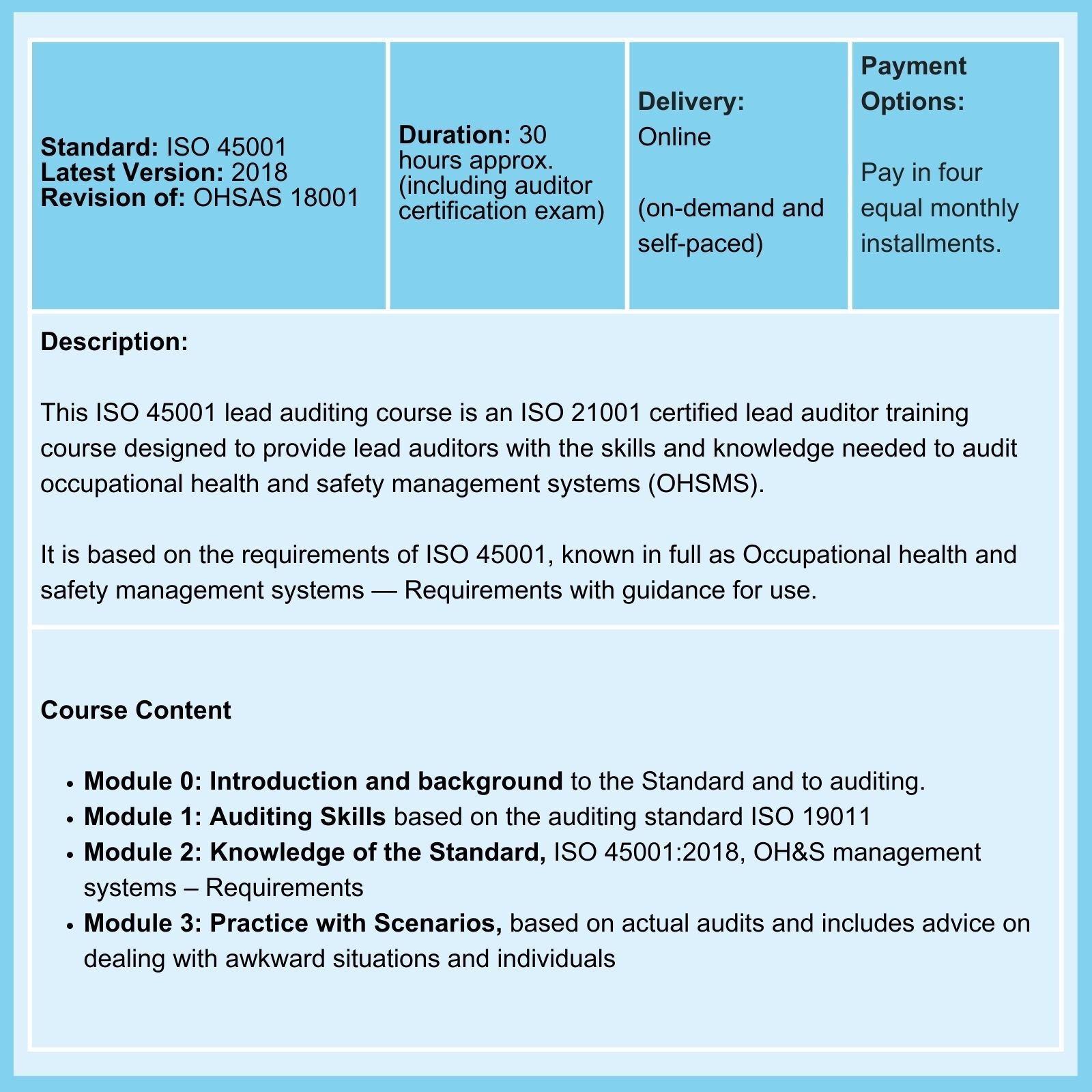
We offer Courses in ISO 9001, ISO 13485, ISO 14971, ISO 17025, ISO 27001, ISO 31010, and ISO 45001.