Practical advice on ISO 9001:2015 Clause 6.2 implementation
ISO 9001 Implementation frequently runs into difficulties when addressing the requirements of Clause 6.2. Here's how we think it should be done.
NOTE: While the exact wording may differ from Standard to Standard, the advice given here also applies to ISO 14001, ISO 27001, ISO 45001, and other standards that have the same HLS structure as ISO 9001.
But, first things first...
What are Quality Objectives?
Quality Objectives are defined in ISO 9001:2015 as objectives related to quality. Not very helpful. The definition, as documented in ISO/TS 9002, is better. It says… ‘Quality objectives should be established at relevant functions, levels, and processes, as appropriate, to ensure the effective deployment of the organization’s strategic direction and quality policy.
For example, quality objectives might be set at an operational level for the procurement function or the design process.’
Our Advice: Top management may establish quality objectives at the strategic, tactical, or operational level.
The strategic level includes the highest levels of the organization, and quality objectives can apply to the whole organization. The tactical and operational levels can include quality objectives for specific products, processes, units, or functions within the organization, and they should be compatible with the organization's strategic direction.
How to Set Quality Objectives
Choose Quality Objectives within the scope of the Quality Management System and communicate them to the persons under the organization’s control who can influence their achievement.
Quality objectives do not have to be related to quality assurance, although if this were a problem area, top priority should be given to it when choosing objectives. Objectives such as increasing sales while maintaining the QMS or introducing automation to reduce costs would be acceptable.
The chosen objectives must be measurable and stated clearly. Aspirational statements are not acceptable.
DOs: Achieving Quality Objectives
In addition to setting Quality Objectives, you must also have a plan for achieving them. This must include:
- what will be done;
- what resources will be required;
- who will be responsible;
- when it will be completed;
- how the results will be evaluated.
Results:
A set of Quality Objectives chosen by top management. Also, the documentation of the actions that have to be taken within the QMS to achieve the chosen Quality Objectives are documented in a series of Improvement Projects or similar.
DON'Ts: Mistakes When Setting Quality Objectives
Here, we address the commonly made errors that lead to non-compliance being found during ISO 9001 Audits. Some typical errors include:
- Failure to set measurable objectives.
- No credible plan to achieve the objectives.
- Objectives too narrowly focused – must be set across many functions and levels within the organization.
- Objectives do not relate to the organization (as documented in the fulfillment of Clause 4.1 requirements).
- Objectives do not relate to the needs and expectations of interested parties (as documented in the fulfillment of Clause 4.2 requirements).
- Failure to monitor and/or review the progress being made in achieving the quality objectives – this is usually documented in a management review report.
Examples of Quality Objectives
Here's an example of Quality Objectives as documented in a Management Review…
Continual Improvement & Quality Objectives
The QMS continues to work satisfactorily.
Current Quality Objectives:
- Establish a system to record Staff performance measurement and versatility. A trial will be carried out for the production area.
Action By: M Cahill & Donald Smyth
Due Date: May 2024 (carried forward)
New Quality Objectives:
- Develop top-level Flow Charts for both…
- SAP System – Purchasing Process
- SAP System – Sales Process
This is primarily for training purposes.
Action By: M Cahill
Due Date: May 2024 (carried forward)
- The new Packing System has been introduced. New packing procedures are now required (see CAR 10/15)
Action By: M Cahill
- Remove the reference to the Process Description Master Table from QMS, as it is no longer used.
Action By: M Cahill
Due Date: May 2025
- Five corporate KPIs (mandatory reporting) are adopted as Quality Objectives. These are…
- Loss time injury rate (LTIR)
- On-time delivery (OTD)
- Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO)
- Customer Complaint Rate (CCR)
- Productivity (value-added)
In due course, targets will be assigned to each.
Reference to these KPIs as Quality Objectives will be added to the Quality Manual.
Action by: Omar Ahmed
Due Date: May 2025
Note that the Objectives are not set just when implementing ISO 9001. They are not ‘set in stone’ and will change over time in response to changes in customer and other business requirements.
Conclusion
Quality objectives are a sensible requirement of ISO 9001. They keep the QMS grounded in reality, which is based on the need to ensure the effective deployment of the organization’s strategic direction and quality policy.
Whatever you do, do not choose objectives just to meet the standard’s requirements—choose objectives that are meaningful to the organization and help it achieve its strategic objectives. Be sure that this will be checked during your ISO 9001 Certification Audit.
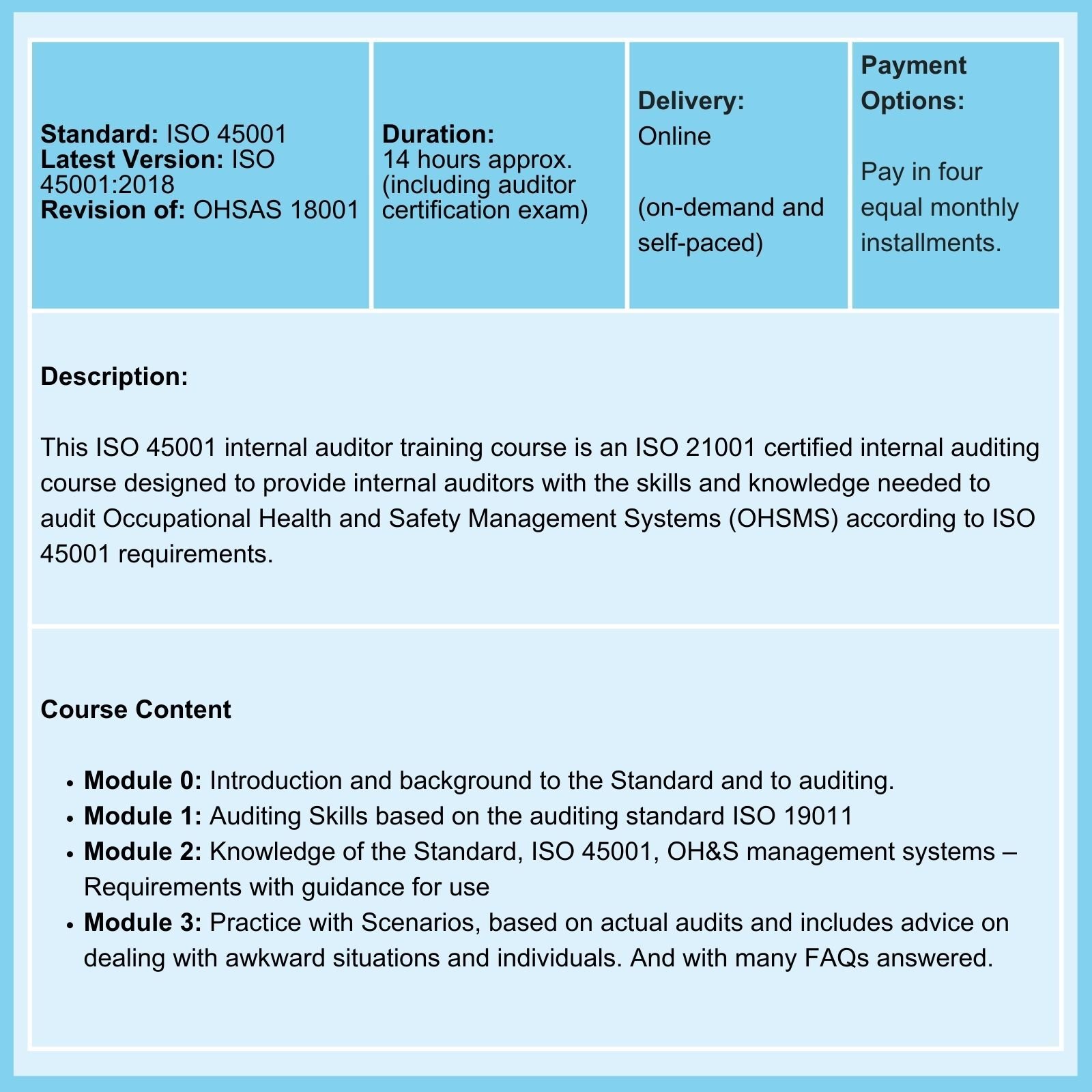
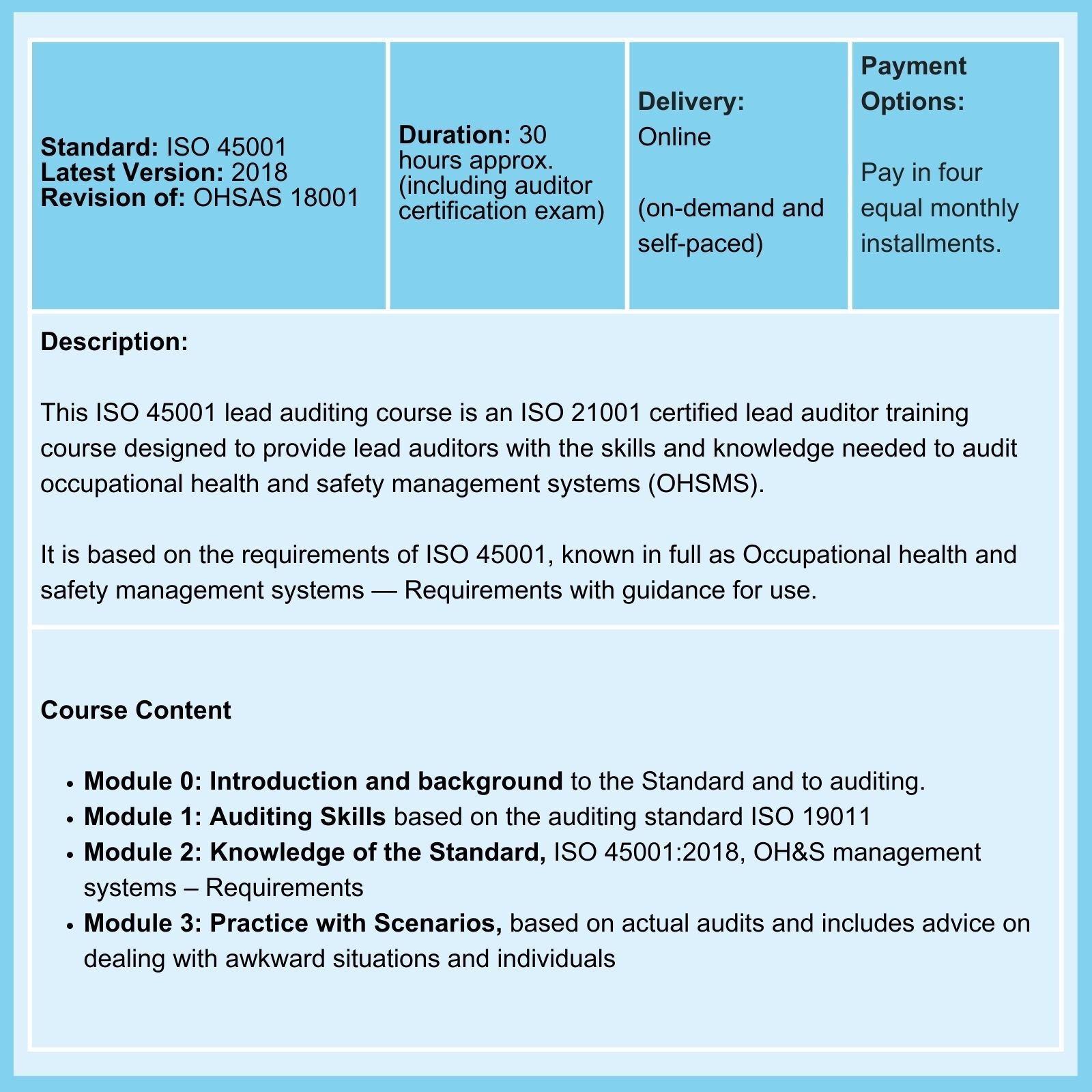
Related Courses
Related Courses
Related Articles
- ISO 9001 Clauses
- ISO 9001 Continual Improvement: DO's and DON'Ts
- ISO 9001 Analysis and Evaluation: DOs and DON'Ts
- ISO 9001 Knowledge Management: DOs and DON'Ts
- ISO 9001 Certification: 20 FAQs Answered
deGRANDSON Global is an ISO Certified Educational Organization
In October 2021, we secured certification to three education-related ISO Standards. We now have a university-grade management system in place conforming to the requirements of …
We have chosen ISO 21001 certification because, unlike IRCA and Exemplar badges (which, in our opinion, are commercially compromised), it is based on independent third-party assessment. It is a ‘university grade’ standard used globally by schools, colleges, and universities to demonstrate competence.
We provide Courses for ISO 9001, ISO 13485, ISO 14001, ISO 17025, ISO 27001, ISO 45001, Risk Management, Data Protection, and more.